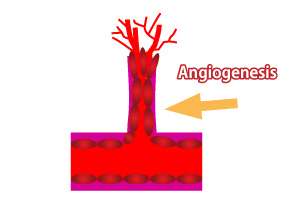
Angiogenesis is the term used to describe the development of new blood vessels derived from ‘angio’ meaning blood and ‘genesis’ meaning birth.
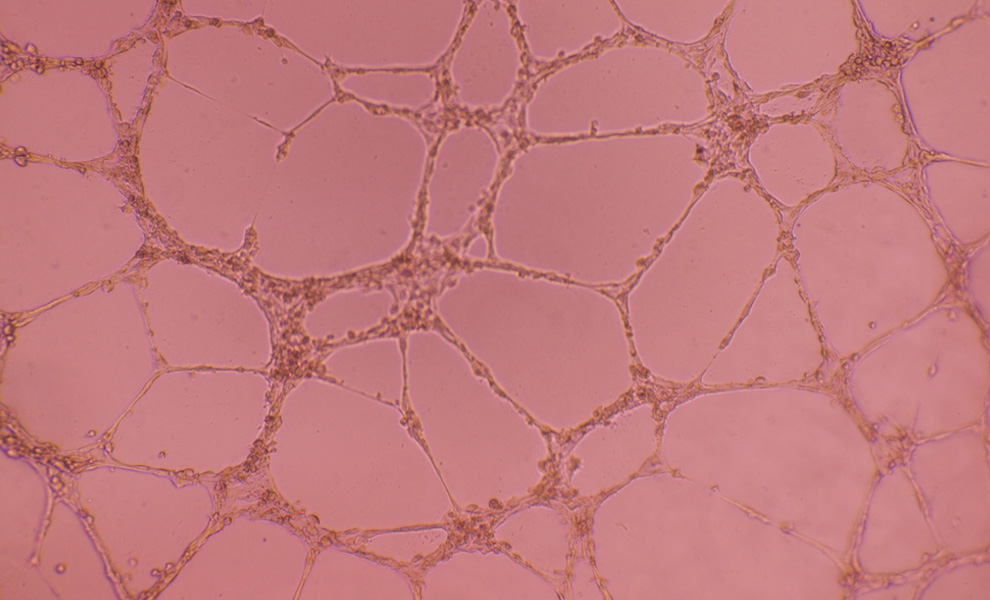
The phenomenon when networks of new blood vessels are generated.The new blood vessels grow from the existing blood vessels.
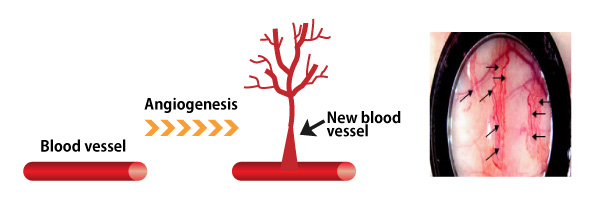
Angiogenesis is an important, natural function in the body responsible for a wide range of activities connected with the circulatory system.
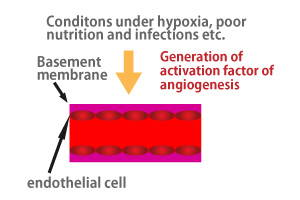
Activating factor of angiogenesis (such as VEGF and MMP) is generated due to growth of cell proliferation, hypoxia condition resulting from infections, blood circulation and deteriorating nutritional condition.
Basement membrane starts melting, then endothelial cells increase and move.
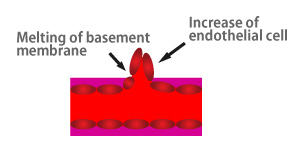
New blood vessel is generated by formation of lumen and basement membrane.
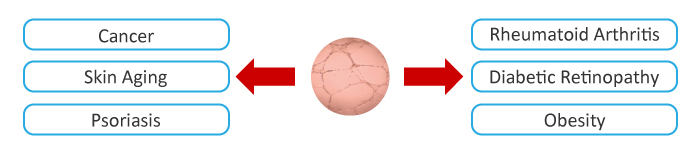
However, in common with all the other functions in the body, when angiogenesis is overstimulated problems develop and angiogenesis is a “common denominator” shared by diseases affecting more than one billion people worldwide. This includes Tumors, Skin Aging, Psoriasis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Obesity, Diabetic Retinopathy and more than 70 other major health conditions affecting children and adults in developed and developing nations.
Anti-angiogenesis therapies are important mediators in many diseases and research to discover new angiogenesis inhibitors is increasing to the extent that it will have a similar impact in the 21st century to that of antibiotic research in the 20th century.