Articles
Angiogenesis in skin disorders

Human skin is exposed daily to solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation, infrared rays and heat, and these stimuli are known to induce skin angiogenesis.
Angiogenesis and skin photoaging
Inflammation, wrinkling of the skin and melanin production occur as a result of exposure to ultraviolet rays. With over exposure, reactive oxygen species can be produced and these break down the extracellular matrix, in particular collagen.
The appearance of unsightly blood vessels in the skin occurs due to ultraviolet stimulation of angiogenesis. Skin photoaging and angiogenesis of the skin are closely related and suppression of photoaging in the skin can be achieved by inhibiting angiogenesis.
See more about angiogenesis and skin wrinkling.
Relationship of Angiogenesis and Wrinkles in skin
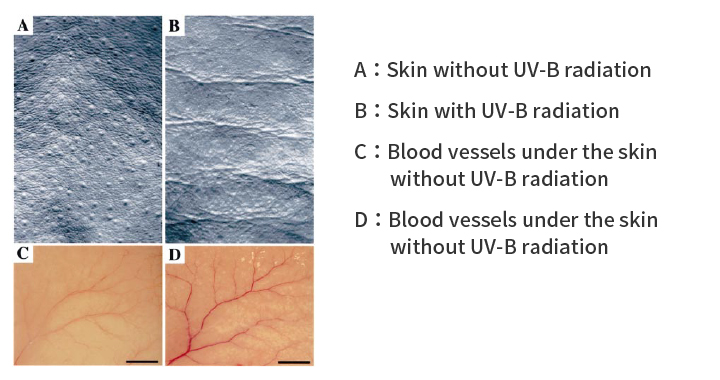
Ref: J Invest Dermatol 118:800- 805, 2002.
Angiogenesis and Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disorder with angiogenic changes. It is characterized by excessive dermal angiogenesis. Uncontrolled angiogenesis, epidermal cell proliferation and localized chronic inflammation result in the formation of a psoriatic plaque.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
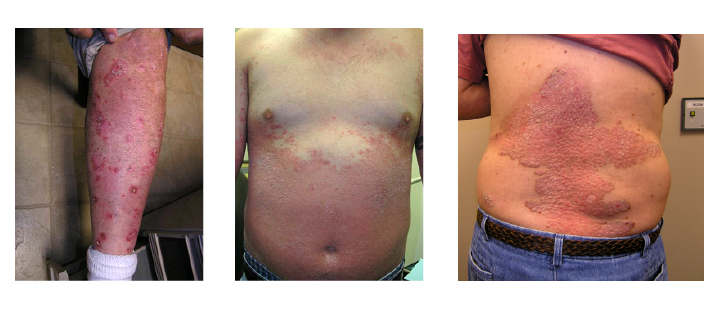
Provided by: S. Grolom, Grikin Skin Inst, Michigan, USA
The cause of psoriasis is not known, but it is believed to have a genetic component. Several factors are through to aggravate psoriasis. These include stress, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking.
The use of agents that target vascular changes represents a novel therapeutic strategy in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
References
- Velasco P; Lange-Asschenfeldt B. Dermatological aspects of angiogenesis. British Journal of Dermatology 2002 Nov; 147(5): 841-852.
- Detmar M; Brown LF; Claffey KP; Yeo KT; Kocher O; Jackman RW; Berse B; Dvorak HF. Overexpression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in psoriasis. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):1141-1146.
- Chung JH; Eun HC. Angiogenesis in skin aging and photoaging. J Dermatol 2007 Sep;34(9):593-600
- D. Graceffa; E. Maiani; A. Pace; F. M. Solivetti; F. Elia; C. De Mutiis; C. Bonifati. Psoriatic Arthritis during Treatment with Bevacizumab for Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma. Case Reports in Rheumatology. Volume 2012 (2012).
- Kawada S; Ohtani M; Ishii N. Increased oxygen tension attenuates acute ultraviolet-B-induced skin angiogenesis and wrinkle formation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Aug;299(2). R694-701.
- Chung JH; Yano K; Lee MK; Youn CS; Seo JY; Kim KH; Cho KH; Eun HC; Detmar M. Differential Effects of Photoaging vs Intrinsic Aging on the Vascularization of Human Skin. Arch Dermatol. 2002 Nov;138(11):1437-1442
- Kiichiro Yano, Hajimu Oura and Michael Detmar. Targeted Overexpression of the Angiogenesis InhibitorThrombospondin-1 in the Epidermis of Transgenic Mice Prevents Ultraviolet-B-Induced Angiogenesis and Cutaneous Photo-Damage. Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2002) 118, 800–805
Related Resources
-

Macolipin (Lipid chiết xuất từ cá mập)
-

Lipid từ đại dương và Lecithin lòng đỏ trứng



